Your Location:Home > Products > chemicals for Plastic additives > Diethyl phthalate(DEP)
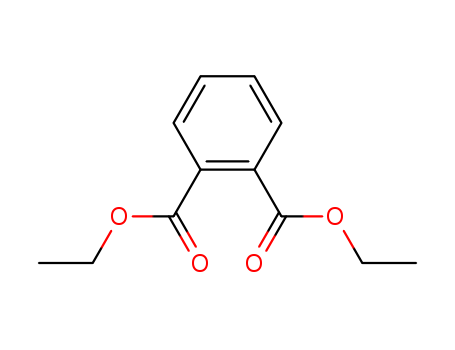


CasNo: 84-66-2
MF: C12H14O4
Appearance: clear oily liquid
|
Production Methods |
Diethyl phthalate is produced by the reaction of phthalic anhydride with ethanol in the presence of sulfuric acid. |
|
Air & Water Reactions |
Insoluble in water. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
Diethyl phthalate is an ester. Esters react with acids to liberate heat along with alcohols and acids. Strong oxidizing acids may cause a vigorous reaction that is sufficiently exothermic to ignite the reaction products. Heat is also generated by the interaction of esters with caustic solutions. Flammable hydrogen is generated by mixing esters with alkali metals and hydrides. Can generate electrostatic charges. [Handling Chemicals Safely 1980. p. 250]. |
|
Health Hazard |
Diethyl phthalate exhibited low to very lowacute toxicity in laboratory animals. Inges tion produced somnolence and hypotension.Inhalation of its vapors may result in lacrima tion, coughing, and irritation of the throatin humans. The oral LD50 value in mice is6170 mg/kg. Diethyl phthalate administeredto pregnant rats at 5% concentration in thefeed showed no adverse effect upon embryoor fetal growth, viability, or the incidence ofmalformations (Price et al. 1988). |
|
Fire Hazard |
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Irritating vapors of unburned chemical may form in fire. |
|
Flammability and Explosibility |
Nonflammable |
|
Pharmaceutical Applications |
Diethyl phthalate is used as a plasticizer for film coatings on tablets, beads, and granules at concentrations of 10–30% by weight of polymer. Diethyl phthalate is also used as an alcohol denaturant and as a solvent for cellulose acetate in the manufacture of varnishes and dopes. In perfumery, diethyl phthalate is used as a perfume fixative at a concentration of 0.1–0.5% of the weight of the perfume used. |
|
Contact allergens |
This plasticizer increases the fexibility of plastics. It is also contained in deodorant formulations, perfumes, emollients, and insect repellents. It can cross-react with dimethyl phthalate. |
|
Safety Profile |
Poison by intravenous route. Moderately toxic by ingestion, subcutaneous, and intraperitoneal routes. Human systemic effects by inhalation: lachrymation, respiratory obstruction, and other unspecified respiratory system effects. An eye irritant and systemic irritant by inhalation. An experimental teratogen. Other experimental reproductive effects. Narcotic in hgh concentrations. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame. To fight fire, use water spray, mist, foam. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes. |
|
Safety |
Diethyl phthalate is used in oral pharmaceutical formulations and is generally regarded as a nontoxic and nonirritant material at the levels employed as an excipient. However, if consumed in large quantities it can act as a narcotic and cause paralysis of the central nervous system. Although some animal studies have suggested that high concentrations of diethyl phthalate may be teratogenic, other studies have shown no adverse effects. LD50 (guinea pig, oral): 8.6g/kg LD50 (mouse, IP): 2.7g/kg LD50 (mouse, oral): 6.2g/kg LD50 (rat, IP): 5.1g/kg LD50 (rat, oral): 8.6g/kg |
|
Source |
Leaching from PVC piping in contact with water (quoted, Verschueren, 1983). |
|
Environmental fate |
Biological. A proposed microbial degradation mechanism is as follows: 4-hydroxy-3- methylbenzyl alcohol to 4-hydroxy-3-methylbenzaldehyde to 3-methyl-4-hydroxybenzoic acid to 4-hydroxyisophthalic acid to protocatechuic acid to β-ketoadipic acid (Chapman, 1972). In anaerobic sludge, diethyl phthalate degraded as follows: monoethyl phthalate to phthalic acid to protocatechuic acid followed by ring cleavage and mineralization (Shelton et al., 1984). Photolytic. An aqueous solution containing titanium dioxide and subjected to UV radiation (λ >290 nm) produced hydroxyphthalates and dihydroxyphthalates as intermediates (Hustert and Moza, 1988). Chemical/Physical. Under alkaline conditions, diethyl phthalate will initially hydrolyze to ethyl hydrogen phthalate and ethanol. The monoester will undergo hydrolysis forming o-phthalic acid and ethanol (Kollig, 1993). A second-order rate constant of 2.5 x 10-2/M?sec was reported for the hydrolysis of diethyl phthalate at 30 °C and pH 8 (Wolfe et al., 1980). At 30 °C, hydrolysis halflives of 8.8 and 18 yr were reported at pH values 9 and 10-12, respectively (Callahan et al., 1979). |
|
storage |
Diethyl phthalate is stable when stored in a well-closed container in a cool, dry place. |
|
Purification Methods |
Wash the ester with aqueous Na2CO3, then distilled water, dry (CaCl2), and distil it under reduced pressure. Store it in a vacuum desiccator over P2O5. [Beilstein 9 IV 3172.] |
|
Incompatibilities |
Incompatible with strong oxidizing materials, acids, and permanganates. |
|
Regulatory Status |
Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (oral capsules, delayed action, enteric coated, and sustained action tablets). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients. |
|
Physical properties |
Clear, colorless, oily liquid with a mild, chemical odor. Bitter taste. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: The diethyl ester of benzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid. |
|
General Description |
A clear, colorless liquid without significant odor. More dense than water and insoluble in water. Hence sinks in water. Primary hazard is to the environment. Spread to the environment should be immediately stopped. Easily penetrates soil, contaminates groundwater and nearby waterways. Flash point 325°F. Severely irritates eyes and mildly irritates skin. Used in the manufacture of perfumes, plastics, mosquito repellents and many other products. |
InChI:InChI:1S/C12H14O4/c1-3-15-11(13)9-7-5-6-8-10(9)12(14)16-4-2/h5-8H,3-4H2,1-2H3
Mesoporous solid acid catalysts with par...
The invention relates to a compound with...
Lignin is one of the most abundant biopo...
A highly water-dispersible heterogeneous...
The valorization of lignin has significa...
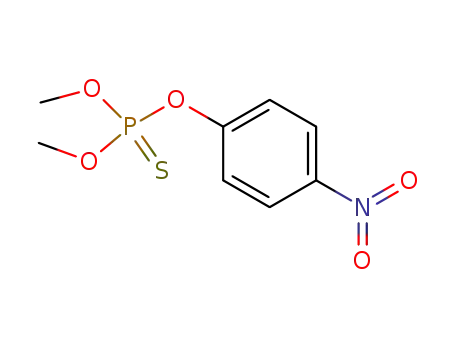
parathion-methyl

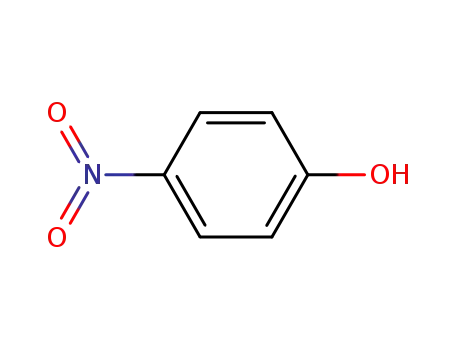
4-nitro-phenol

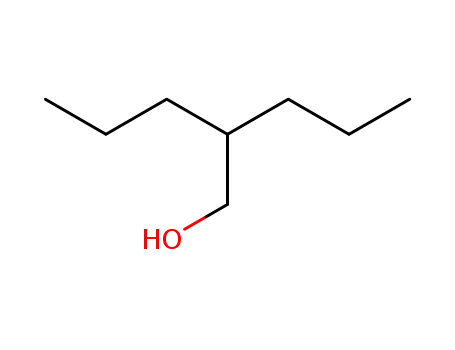
2-propyl-1-pentanol

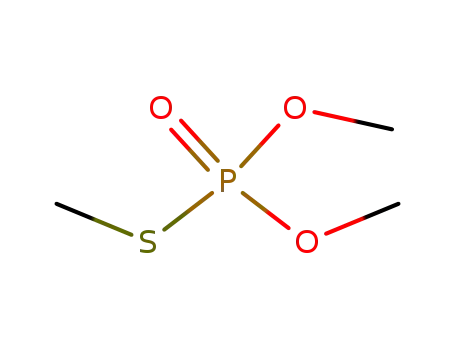
O,O,S-trimethyl phosphorothioate

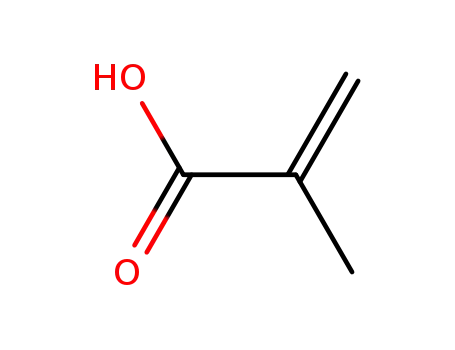
poly(methacrylic acid)

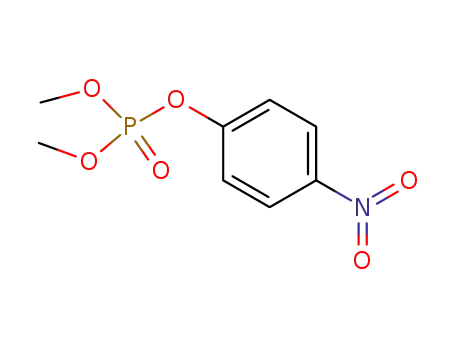
methyl paraoxon

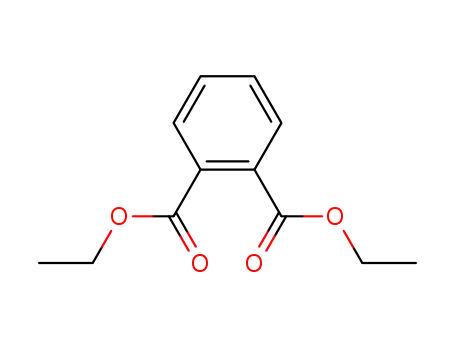
Diethyl phthalate

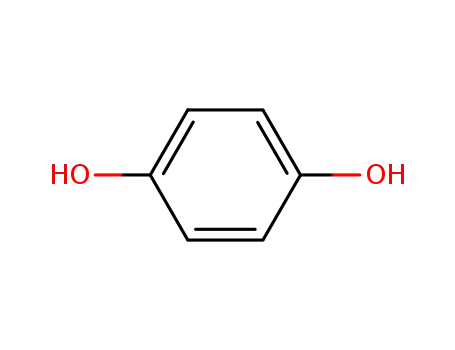
hydroquinone

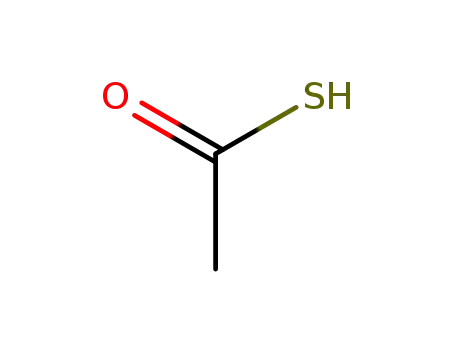
tiolacetic acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
oxygen;
at 22.2 - 25.3 ℃;
Wavelength;
Kinetics;
Quantum yield;
UV-irradiation;
Neat (no solvent);
|
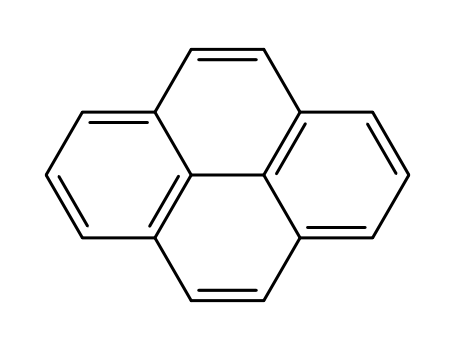
pyrene

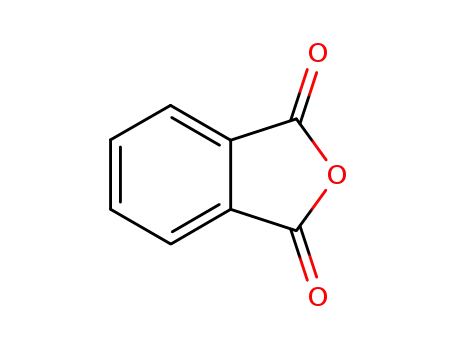
phthalic anhydride

xanth-9-one

pentadecane

n-docosane

n-hexacosane

tetradecane

Hexadecane

Diethylene glycol monobutyl ether

n-butyl isobutyrate

heneicosane

n-tricosane

tetracosane

n-pentacosane

![cyclopenta[def]phenanthrene](/upload/2025/4/1e16d8ad-1678-43cb-91e7-f8b74b96d0d4.png)
cyclopenta[def]phenanthrene

1,2-benzenedicarboxylic acid diisooctyl ether

2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methyl-phenol


Diethyl phthalate

Phthalic acid dibutyl ester

![4H-Cyclopenta[def]phenanthrene](/upload/2025/4/28399f5b-0c0a-4f84-9f9a-65b902777bc8.png)
4H-Cyclopenta[def]phenanthrene

benzyl n-butyl phthalate

1,1'-Biphenyl-2,2',6,6'-tetracarboxaldehyde


4,5-phenanthrene-8,9-dicarbaldehyde

1-hexadecylcarboxylic acid

6-propyltridecane
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
oxygen; ozone;
In
water;
for 0.25 - 2h;
|

phthalic anhydride
tetraethoxy orthosilicate
diethyl sulphite
ethanol
phthalic acid dimethyl ester

phthalic acid bis-(2-trimethylsilanyloxy-ethyl ester)
bindone
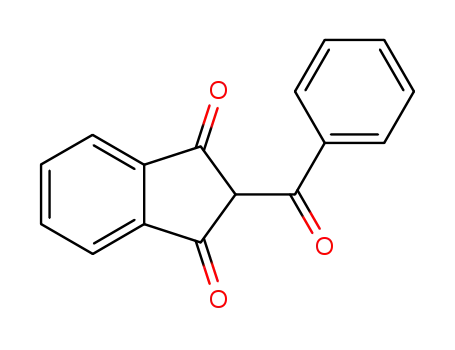
2-benzoyl-1,3-indanedione