Your Location:Home > Products > chemicals for Printing and dyeing > Thiourea
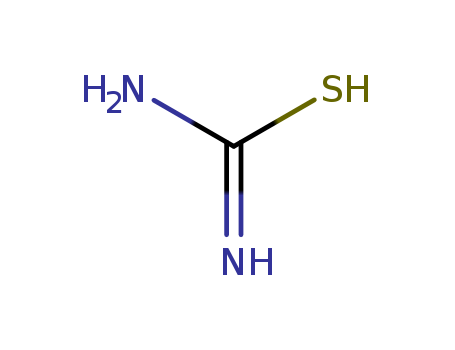


CasNo: 62-56-6
MF: CH4N2S
Appearance: white crystals or powder
|
Production Methods |
Thiourea is formed by heating ammonium thiocyanate at 170 °C (338 °F). After about an hour, 25% conversion is achieved. With HCl, thiourea forms thiourea hydrochloride; with mercuric oxide, thiourea forms a salt; and with silver chloride, it forms a complex salt. |
|
Preparation |
Thiourea is manufactured by heating ammonium thiocyanate at 140-145°C for about 4 hours; equilibrium is established when about 25% of the thiocyanate is converted to thiourea.Thiourea may also be prepared by the interaction of cyanamide and hydrogen sulphide:Thiourea closely resembles urea in that reaction with formaldehyde gives methylol derivatives and then resinous condensates which on continued heating yield network structures. Thiourea-formaldehyde resins are slower curing than urea-formaldehyde resins and the hardened products are more brittle and more water-resistant. At one time thiourea-formaldehyde resins were added to urea-formaldehyde resins to give mouldings and laminates with improved water-resistance. These mixed resins have now been largely superseded by melamine-formaldehyde resins which give products with better resistance to heat. |
|
Air & Water Reactions |
Water soluble. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
Thiocarbamide is a white crystalline material or powder, toxic, carcinogenic. When heated to decomposition Thiocarbamide emits very toxic fumes of oxides of sulfur and oxides of nitrogen. Violent exothermic polymerization reaction with acrylaldehyde (acrolein) [MCA SD-85, 1961], violent decomposition of the reaction product with hydrogen peroxide and nitric acid [Bjorklund G. H. et al., Trans. R. Soc. Can.,1950, 44, p. 28], spontaneous explosion upon grinding with potassium chlorate [Soothill, D., Safety Management, 1992, 8(6), p. 11]. |
|
Hazard |
A questionable carcinogen. May not be used in food products (FDA); skin irritant (allergenic). |
|
Health Hazard |
Poisonous inhaled or swallowed. Irritating to skin; may cause allergic skin eruptions. |
|
Fire Hazard |
Noncombustible solid. There is no report of any explosion resulting from reactions of thiourea. Small amounts of thiourea in contact with acrolein may polymerize acrolein, which is a highly exothermic reaction. |
|
Contact allergens |
Thiourea is used as a cleaner agent for silver and cop- per, and as an antioxidant in diazo copy paper. It can induce (photo-) contact dermatitis. |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
Thiourea is a free radical scavenger of the peroxide radical. It was shown to inhibit lipid peroxidation and ultraviolet (UV)-induced crosslinking of collagen. Bud dormancy in plants can be inhibited by thiourea, which is used as a growth stimulator. It is also known to be used in the treatment of hyperthyroidism. |
|
Potential Exposure |
Thiourea is used as rubber antiozonant, toning agent; corrosion inhibitor; and in pharmaceutical manufacture; in the manufacture of photosensitive papers; flame-retardant textile sizes; boiler water treatment. It is also used in photography; pesticide manufacture; in textile chemicals. |
|
Carcinogenicity |
Thiourea is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in experimental animals. |
|
Purification Methods |
Crystallise thiourea from absolute EtOH, MeOH, acetonitrile or water. Dry it under vacuum over H2SO4 at room temperature. [Beilstein 3 IV 342.] |
|
Incompatibilities |
Dust may form explosive mixture with air. Reacts violently with acrolein, strong acids (nitric acid). Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. |
|
Definition |
A colorless crystalline organic compound (the sulfur analog of urea). It is converted to the inorganic compound ammonium thiocyanate on heating. It is used as a sensitizer in photography and in medicine. |
|
General Description |
White or off-white crystals or powder. Sinks and mixes with water. |
|
Agricultural Uses |
Thiourea is a sulphur analogue of urea. It is a crystalline and colorless solid which is relatively insoluble in water. Thiourea, capable of breaking the dormancy of seeds, is used to stimulate seed germination. Seeds are soaked for less than 24 hours before planting. |
InChI:InChI=1/CH4N2O4S/c2-1(4)3-8(5,6)7/h(H3,2,3,4)(H,5,6,7)
The C-S cross coupling of pharmaceutical...
Substituted N-substituted alkoxyphenyl c...
Novel boronic acid and ester and carboxy...
Compounds of formula (I) STR1 wherein R ...
isothiocyanic acid

thiourea
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
ammonia;
|


thiourea
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
entspr. Diamin + CS2;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5.92 g (94.4%) |
|
|
|
|
|
6.05 g (95.9%) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.10 g (98.3%) |

isothiocyanic acid
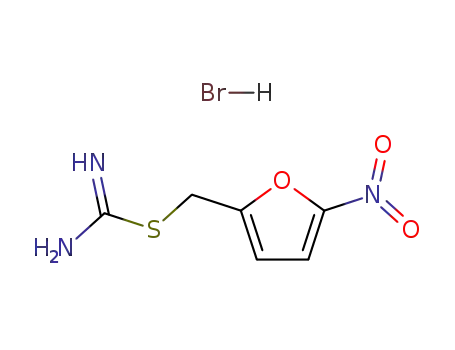
(5-nitrofuran-2-yl)methyl carbamimidothioate hydrobromide
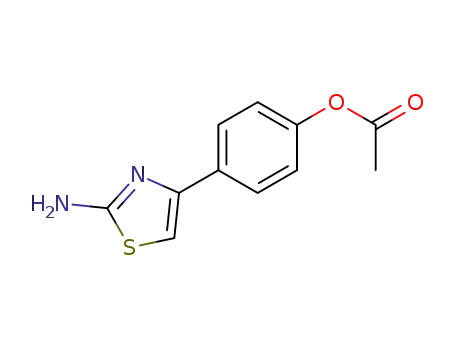
4-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)phenyl acetate
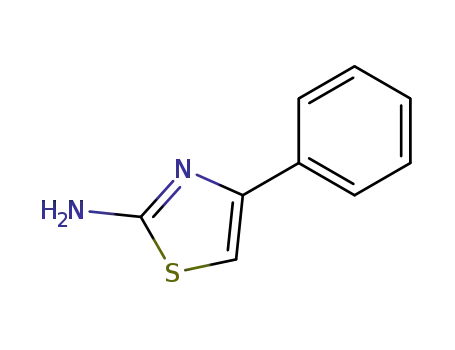
2-Amino-4-phenylthiazole
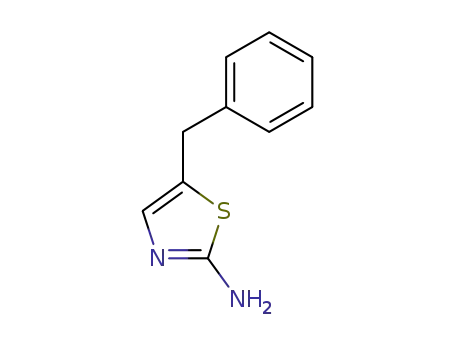
5-(phenylmethyl)-1,3-thiazol-2-amine